Factors Causing Atopic Dermatitis and Treatments for it
Have you ever felt rashes on your skin that leave you itchy and irritated? Atopic dermatitis, or eczema, might be the reason. It is a common skin disease that affects a majority of individuals without their knowledge. What seems as dry, flaky skin caused by weather changes may be a symptom of this eczema. It may look normal, but isn’t and can get worse with the passage of time.
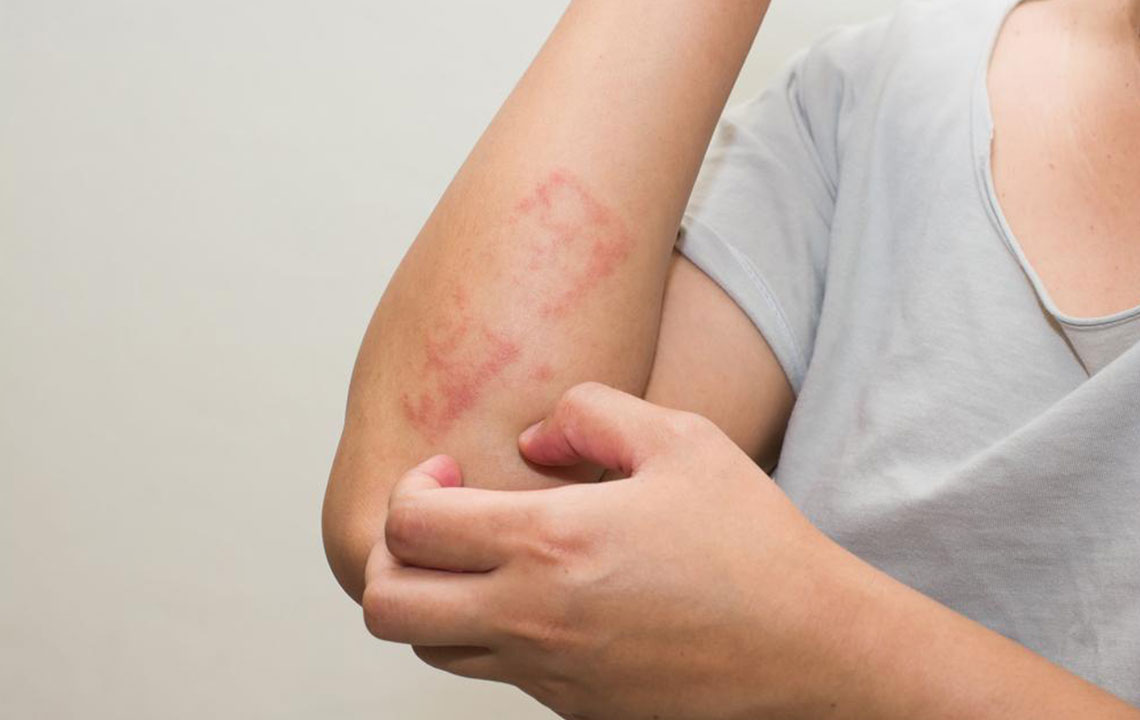
Atopic dermatitis, or atopic eczema, is characterized by the swelling of the skin tissue. In children, the outbursts can be found on cheeks. In adults, they are found in front of the elbows or behind the knees.
There is no specific cause behind the onset of this ailment. However, the following factors may contribute towards atopic dermatitis or eczema:
Heredity – An individual is likely to be affected by atopic dermatitis or eczema if it is present in his genes.
Environment – In some cases, exposure to dust, pollens, and other allergens can trigger this eczema.
Food – A few individuals are sensitive to certain food items, for, example, wheat. Consumption of these can cause atopic dermatitis or eczema outbursts.
Humidity – People living in areas having dry climate are more prone to this disease. Low humidity can suck moisture away from the skin.
Hard water – Hard water, containing a high level of carbonates of calcium and magnesium may also inflame the skin.
Atopic dermatitis or eczema symptoms include dryness of the skin which may be accompanied with flakes. Red patches around the neck and on the eyelids are a common sight. Excessive itching may take place resulting in the urge to scratch, which may worsen the condition. There can be rashes all over the body with cuts and abrasions in some areas. If the cuts get infected, it is advisable to seek a doctor at the earliest.
Atopic dermatitis or eczema does not require any specific tests for its diagnosis. The diagnosis involves visual observation of the symptoms, assessment of family history, and scrutiny of allergies. At times, a skin biopsy might also be conducted to determine any underlying factor behind eczema. It involves conducting a thorough examination of a part of skin tissue with the help of a microscope. A prick test may also prove helpful if the disease is augmented by allergens.It involves pricking a bump filled with infected liquid.
There are no permanent treatment options for atopic dermatitis or eczema. However, its impact can be reduced by using some treatments. The following methods can be used to manage atopic dermatitis or eczema:
Medicine – Corticosteroid and pimecrolimus are a few medicines used for reducing inflammation. These are very strong and should be used under the guidance of a doctor. Dupilumab may also soon be rolled out for the treatment of atopic dermatitis.
Phototherapy – This method involves subjection to ultraviolet rays and is used as a long-term treatment. It should be moderately used as it can lead to skin cancer.
Immunosuppressants and antidepressants – Ciclosporin, an immunosuppressive drug is an alternative treatment option for atopic dermatitis or eczema. Antidepressants provide relief from itching. However, they should only be taken if prescribed by the doctor.
Skincare – It is essential to use mild lotions and creams to prevent the skin from drying. Harsh soaps and hot water are strictly not recommended. Strong fragrances also irritate the skin and should, thus, not be used.
Lifestyle – Wear soft, cool fabrics in summers. An increased amount of liquid intake keeps the skin supple. Consumption of foods rich in vitamin D might also be helpful. If you are allergic to a particular item, strike it off from your diet. Most importantly, stay happy and avoid undue stress.
Atopic dermatitis or eczema gets exacerbated when accompanied by asthma and hay fever. These problems are caused by a malfunction in the immune system. It is important to treat them side by side as they can make management of the eczema complex. Also, extra care should be taken while going outdoors. Wearing full sleeves clothes can prohibit exposure of the skin to pathogens. Scratching can lead to the skin getting scraped off, so, should be avoided. Ruptured bumps that ooze out liquid are a potential source of infections.
Atopic dermatitis is a serious type of eczema. Its symptoms should not be ignored. Nipping the disease right in childhood can prevent its escalation in the future. Also, early treatment reduces the chances of development of asthma. If you or your child experience two or more typical symptoms of atopic dermatitis or eczema, a good dermatologist will come to your rescue. He will provide you with the necessary medication and also guide you towards its effective management.

